Abstract
Introduction
Among patients able to tolerate intensive induction, standard acute myeloid leukemia (AML) induction therapy is a regimen referred to as "7+3," consisting of 7 days of intravenous cytarabine and 3 days of daunorubicin (DNR) or idarubicin (IDA). Targeted therapies may be added to the 7+3 backbone. In the pivotal trial establishing midostaurin as standard of care for induction in FLT3-mutated AML (RATIFY trial), DNR 60 mg/m2 was the anthracycline used (Stone et al. NEJM 2017). There is limited information on use of IDA in combination with midostaurin. This multicenter, retrospective study assessed efficacy and toxicity associated with midostaurin and IDA-based 7+3 induction, using the findings of the RATIFY trial as a historical comparator.
Methods
We collected cases from 5 academic institutions. At each institution, a report was generated through the electronic medical record identifying patients who initiated IDA-based 7+3 with midostaurin induction therapy between April 1, 2017 and December 31, 2020. Data collected from eligible patients' charts were recorded in a REDCap database hosted by the University of Utah. At each institution, research was exempted by the respective IRBs.
The primary objective was CR rate after midostaurin and IDA-based 7+3 induction compared to DNR-based 7+3 as reported in the RATIFY trial. CR was attained if patients met all of the following criteria: less than 5% bone marrow blasts, absence of extramedullary leukemia, an absolute neutrophil count of ≥ 1000/µL, a platelet count of ≥ 100,000/µL, and the absence of blasts in the peripheral blood. The secondary objective was EFS, defined as time to relapse, mortality, or failure to achieve CR by day 60. Secondary objectives included assessment of hematologic and non-hematologic toxicities. Adverse events (AEs) were graded per CTCAE version 4.03 to match the grading system used in the RATIFY trial.
Data were analyzed against the RATIFY trial as a historical comparator. A 2-sided, 1-sample binomial test was used to compare CR rate to the reported 58.9% CR rate in RATIFY, with alpha = 0.05. In order to detect a 20% relative increase in CR rate, with 80% power and alpha of 0.05, 131 patients would need to be reviewed. Descriptive statistics were used for demographic data, Kaplan-Meier estimates were used for time to event data, and Fisher exact tests were used to compare AE rates.
Results
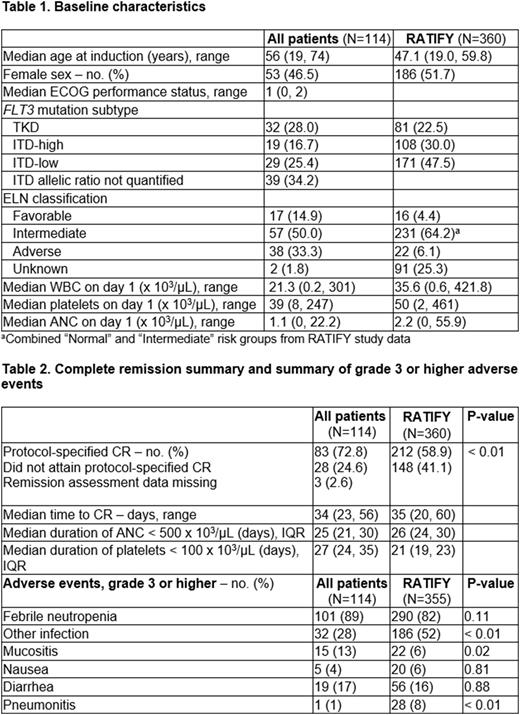
In all, 114 patients were included across 5 sites. Baseline characteristics (Table 1) show median age at induction was 56 years (19, 74), with a median duration of follow-up of 18.1 months (0.5, 51.3). Thirty-two patients (28%) had FLT3-TKD mutations, and 87 (76%) had FLT3-ITD mutations. Eighty-eight (78%) completed a 14-day midostaurin course. Eleven of 114 (9%) received midostaurin dose reduction due to drug interactions and 2 (1.8%) received dose reduction due to toxicity. Twenty-four (21%) received G-CSF during induction. Midostaurin was given during consolidation to 74 patients (64.3%). Seventy-four (64.3%) proceeded to allogeneic stem cell transplant, and 13 (11.4%) received maintenance midostaurin post-transplant.
Of the 114 patients who underwent induction with midostaurin and IDA-based 7+3, 83 (72.8%) achieved CR (Table 2). Median time to CR was 34 days, similar to the time to CR reported in the RATIFY study. Median duration of neutropenia was 25 days, and median duration of thrombocytopenia was 27 days (Table 2). Median EFS was 11.7 months, compared with 8.4 months in the RATIFY trial (Figure 1).
Table 2 shows rates of grade 3 or higher AEs. IDA-based 7+3 induction with midostaurin appeared to have a similar toxicity profile to DNR-based 7+3 induction as reported in the RATIFY trial; however, there appeared to be a lower rate of other infections in the IDA population.
Conclusion
This multicenter, retrospective study describes the largest series of FLT3-mutated AML patients treated with IDA and midostaurin. There was a statistically significant higher CR rate and a longer EFS with IDA/midostaurin compared with DNR/midostaurin as reported in the RATIFY trial. The toxicity profile of midostaurin with IDA-based 7+3 induction appeared similar to previously reported data. A limitation of this study is its retrospective nature, but these results suggest IDA may be the preferred anthracycline in combination with midostaurin in FLT3-mutated AML.
Disclosures
Wagner:Abbvie Inc.: Other: Partner is currently employed as a Medical Science Liaison . Kurish:Market Access Transformation: Honoraria. Lo:Oncopeptides: Consultancy; EUSA Pharma: Consultancy. Kovacsovics:Abbvie: Research Funding; Caelum: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Glycomimetics: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Syndax: Research Funding; Kite: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal